Introduction
By no means complete, October’s mini guide that follows provides notes for exploring various interesting deep sky objects (DSOs) and lists other items of interest useful to the amateur astronomer.
Entries can be interpreted based on designation, description and magnitude as follows.
Designation – Description – Magnitude:
★ Telescopes 10-inch aperture minimum.
★★ Telescopes 6-inch to 9-inch aperture.
★★★ Binoculars (50mm+ aperture) and telescopes
3-inch to 5-inch aperture.
A collimated instrument, favourable atmospheric conditions, dark skies and dark-adapted eyes are assumed.
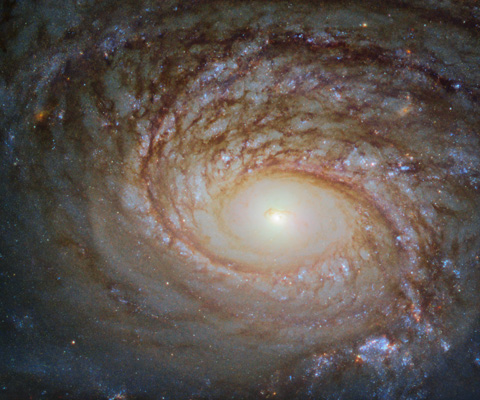

The NGC 772 spiral galaxy.
Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, A. Seth et al.
About NGC 772
The Universe is simply so vast that it can be difficult to maintain a sense of scale.
Many galaxies we see through telescopes such as the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope,
the source of this beautiful Picture of the Week, look relatively similar: spiralling arms,
a glowing centre, and a mixture of bright specks of star formation and dark ripples
of cosmic dust weaving throughout.
This galaxy, a spiral galaxy named NGC 772, is no exception. It actually has much in
common with our home galaxy, the Milky Way. Each boasts a few satellite galaxies,
small galaxies that closely orbit and are gravitationally bound to their parent galaxies.
One of NGC 772’s spiral arms has been distorted and disrupted by one of these satellites
(NGC 770 — not visible in the image here), leaving it elongated and asymmetrical.
However, the two are also different in a few key ways. For one, NGC 772 is both a peculiar
and an unbarred spiral galaxy; respectively, this means that it is somewhat odd in size,
shape, or composition, and that it lacks a central feature known as a bar, which we see in
many galaxies throughout the cosmos — including the Milky Way. These bars are built of gas
and stars, and are thought to funnel and transport material through the galactic core,
possibly fuelling and igniting various processes such as star formation.
Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, A. Seth et al.
Observation guide
| October deep sky objects |
| Andromeda constellation |
|
M31
|
This galaxy is easy to spot because of its large apparent size (3°x1°) and brightness. A 6-inch instrument will show the galaxy’s nucleus where larger instruments will show evidence of dust lanes within its spiral arms.
|
4.5
|
★★★
|
|
M110
|
This dwarf elliptical galaxy is a satellite of the M31 and is viewable in binoculars. It appears as a light patch in larger scopes.
|
10.0
|
★★
|
|
M32
|
Situated by the M31, this dwarf ‘early-type’ galaxy is easy to locate and readily visible in smaller instruments.
|
10.0
|
★★★
|
|
NGC891
|
An edge-on galaxy with an obscuring dust lane along its length. Its overall low surface brightness makes it a difficult object to see. The dust lane will be detected only in larger scopes and CCD cameras.
|
10.9
|
★★
|
|
NGC185
|
A dwarf spheroidal galaxy near the M31.
|
9.19
|
★★
|
|
NGC147
|
Faint dwarf spheroidal galaxy near the M31 and very close to the NGC185. Requires at least 10 inches of aperture to view this galaxy.
|
10.4
|
★
|
| Cassiopeia constellation |
|
M103
|
A bright open cluster of around 40 stars of different magnitudes some of which are hot blue stars. A number of interesting open clusters are situated near the M103 worth looking out for.
|
6.4
|
★★★
|
|
NGC457
|
Known as the Owl Cluster it is situated close to the M103. An open cluster that consists of approximately 150 stars some of which show bright colours, the brightest being 5th and 7th magnitude. Shows best in binoculars and small instruments.
|
6.7
|
★★★
|
|
NGC663
|
A reasonably bright cluster with around 400 stars near the M103.
|
7.10
|
★★★
|
|
NGC7789
|
A beautiful open cluster with over 1,000 stars. In small scopes it appears as a hazy patch but larger instruments can resolve between 100 and 200 stars.
|
8.28
|
★★★
|
| Cetus constellation |
|
M77
|
A near face-on unbarred spiral galaxy with a very bright core where its outer parts are difficult to discern. Instruments of aperture of 6 inches and above will reveal its structure to varying degrees.
|
10.5
|
★★★
|
| Aries constellation |
|
NGC772
|
A spiral galaxy with a bright nucleus. Requires an 8-inch instrument to view.
|
10.9
|
★★
|
| Pisces constellation |
|
M74
|
A face-on spiral galaxy with a low surface brightness and two clearly defined spiral arms. Larger instruments above 8 inches may bring out the graininess of the core and possibly the H-II emissions present in the galaxy’s arms.
|
10.5
|
★★
|
| Triangulum constellation |
|
M33
|
Located in the Triangulum this is a face-on galaxy. It is however a dim galaxy with a small nucleus that requires good conditions to effectively observe. Visible to the unaided eye under perfect conditions.
|
7.0
|
★★★
|
|
NGC604
|
Found in the North-eastern part of the M33 this is a H-II emission region. A number of interesting objects like the NGC588 diffuse nebula, NGC592 emission nebula and NGC595 can be found nearby.
|
13.0
|
★
|
|
|
Designation, Description, Magnitude
|
★ Telescopes 10-inch aperture minimum.
★★ Telescopes 6-inch to 9-inch aperture.
★★★ Binoculars (50mm+ aperture) and telescopes 3-inch to 5-inch aperture.
|
The night sky
Under excellent conditions over 2,000 stars can be seen with the unaided eye but only a few hundred of these are prominent enough to be useful in navigating the night sky, these are normally included in amateur sky maps and digital planetarium programs like the SkySafari, Stellarium, The Sky, Starry Night, Winstars 2 etc. Some stars will show colour that is useful in identifying them. For example, Antares, Betelgeuse and Aldebaran are orange/red where Vega, Rigel and Spica appear as blue/white.
Stars that form easily recognisable patterns have been given names and are referred to as constellations. Of these, the brightest stars act as beacons and can be used to effectively navigate the night sky during the different months of the year. To that extent stars can be particularly useful in locating other interesting objects nearby normally viewable through binoculars or larger instruments.
Planets and their satellites, comets and meteors move independent of the night sky background and at comparatively high speeds. They are therefore very difficult or impossible to reference to any star. However, planets like Jupiter, Saturn, Venus and Mars as well as the Moon are easy to spot with the unaided eye and in the case of the larger planets and especially the Moon, even medium size binoculars will reveal a limited degree of detail.
About NGC 604
At the heart of NGC 604 are over 200 hot stars, much more massive than our Sun (15 to 60 solar masses).
They heat the gaseous walls of the nebula making the gas fluoresce. Their light also highlights the nebula's three-dimensional shape, like a lantern in a cavern.
Credit: Hui Yang (University of Illinois) and NASA/ESA

The NGC 604 nebula. Credit: Hui Yang and NASA/ESA.
Sky conditions
The prevailing sky conditions will have a significant effect on what you can see through any instrument and binoculars. As such if you live near a city the light pollution can make it difficult to locate and observe most DSOs. The Moon and a hazy sky will also have a negative effect.
For best results observe from a dark site and under clear transparent skies without the moon being present. Once your eyes have been accustomed to the dark conditions (this takes around 20-30 minutes) you should be able to enjoy the night sky at its best.
Filters
Filters will help to an extent and lager instruments will benefit more from them. Light pollution filters would help and photo-visual UHC (nebula filters) would be worth considering.
Printed aids
A huge number of printed aids exist in terms of deep sky maps and books. An excellent printed guide for people new in astronomy is The Year-Round Messier Marathon Field Guide published by Willmann Bell Inc.
In this large format hard-back book, the author, Harvard Pennington shows how to:
- Learn 17 bright finder stars and 17 prominent finder constellations so you will know where to look for all 110 Messier objects.
- Align a sighting device such as an 8x50 finder scope or the Telrad® so that you can point your instrument rapidly and with assurance toward all of the Messier objects.
- Calibrate your instrument so that you know exactly how much sky you see through your finder and through the eyepiece of your instrument.
- Find all of the Messier objects using the maps, drawings and descriptions in this book. You will know exactly where to point your instrument, and what the object should look like when you find it.
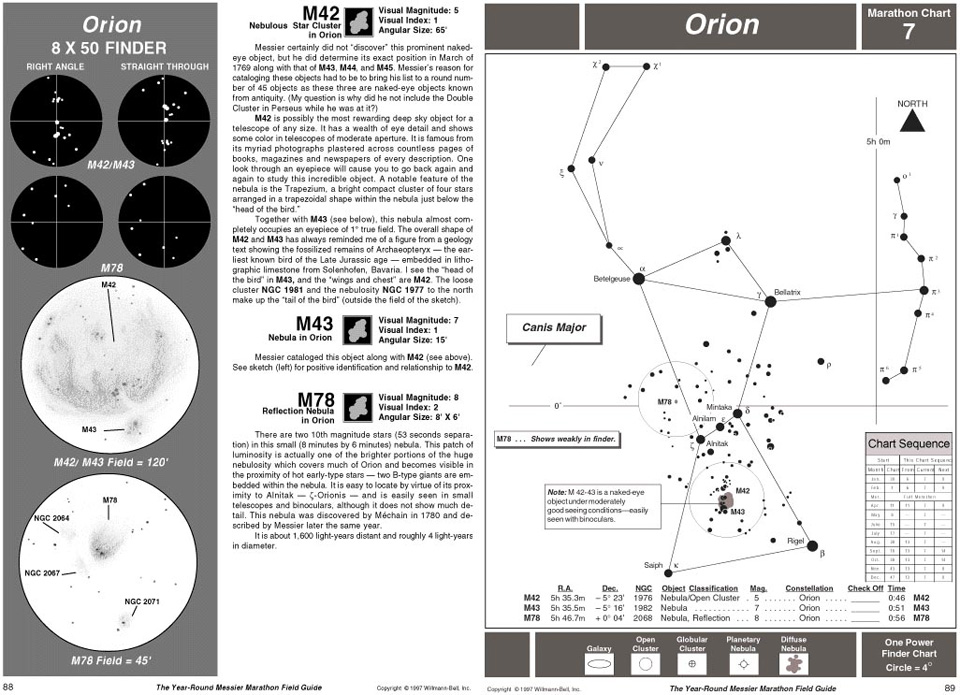
Extract from The Year-Round Messier Marathon Field Guide
published by Willmann Bell Inc.
Related topics:
night sky, deep sky object guide, October



